Antimicrobial agents have historically played a pivotal role in combating infectious diseases in both humans and animals. However, the global community faces twin challenges: inadequate funding for new antimicrobial development, and the escalating threat of antibiotic resistance. While solutions are emerging for funding issues, tackling antibiotic resistance remains formidable due to differing approaches and complexities.
Veterinary advancement in antibiotic management
More so than human medicine, the veterinary sector is proactively addressing the rise of antibiotic resistance and usage through robust farm management practices. Notably, significant reductions in antibiotic use have corresponded with marked decreases in resistance, underscoring the effectiveness of proactive measures.
National monitoring efforts illuminate trends
Belgium has deployed national monitoring programs to track antimicrobial consumption (AMC) and resistance (AMR) across various segments, including humans, food-producing animals, and the food supply chain. As part of the National Action Plan, a ‘One Health’ report on AMC and AMR in Belgium has been generated, offering crucial insights and conclusions.
Comparative analysis of antibiotic consumption
Despite the complexity of comparing antimicrobial use between human and veterinary medicine, analyzing consumption based on active product on biomass provides clarity. Between 2012 and 2021, both sectors recorded decreases, with the veterinary sector outperforming human medicine with a notable 40% reduction. Human medicine shows a decrease of approximately 31%.
Notably, there was a significant decrease in the human sector between 2019 and 2020, followed by an increase in 2021, likely due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and the subsequent return to normal medical practices. In addition, when we look further to 2022, the veterinary industry experienced a significant decrease of 7.5% due to its major efforts. No data has yet been made available for human medicine for 2022 (Figure 1).
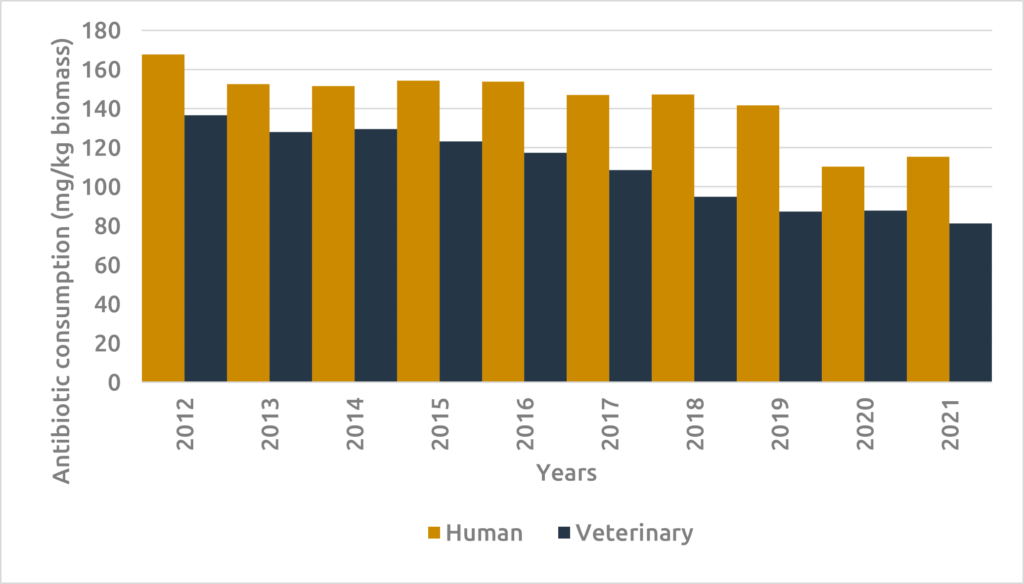
Figure 1: Comparison antibiotic consumption (mg/kg biomass) in human medicine and veterinary medicine (2012-2021) (source: BELMAP2023)
Dynamics of veterinary antibiotic use
A deep dive into trends from 2011 to 2022 underscores remarkable reductions in the veterinary sector, particularly for antibiotics crucial to human medicine. Notable decreases include an 82.7% reduction for fluoroquinolones and 3rd and 4th generation antibiotics, and reductions of 88% and 83.5% for polymyxins and premixes, respectively.
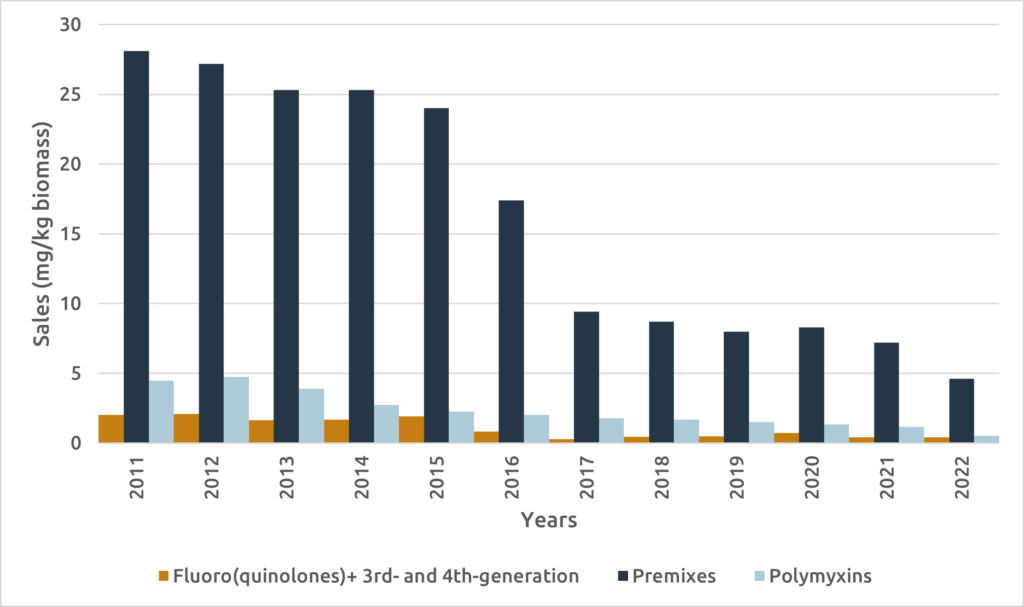
Figure 2: Total sales (mg/kg biomass) from 2011 to 2022 in the veterinary sector for fluoroquinolones and 3rd and 4th generation antibiotics, premixes and polymyxins (source: BELMAP2023)
Data analysis at farm level
In Belgium, antibiotic usage data per sector and animal category have been collected at the farm level since 2018, covering pigs, broilers, laying hens, and veal calves. Analysis of the BD100 (number of treatment days with antibiotics per 100 days) across different animals reveals veal calves and weaned pigs as the highest users, with veal calves showing the most significant reduction in BD100. While pigs lead in absolute tonnages, layers, sows, and sucklers exhibit minimal antibiotic usage (Figure 3).
It’s crucial to consider various factors influencing these differences. For instance, the veal industry’s ‘open farm’ system – in which calves from different sources converge until slaughter – creates higher infection pressure, necessitating increased antibiotic usage compared to the ‘closed farm’ model of the pig and poultry industries.
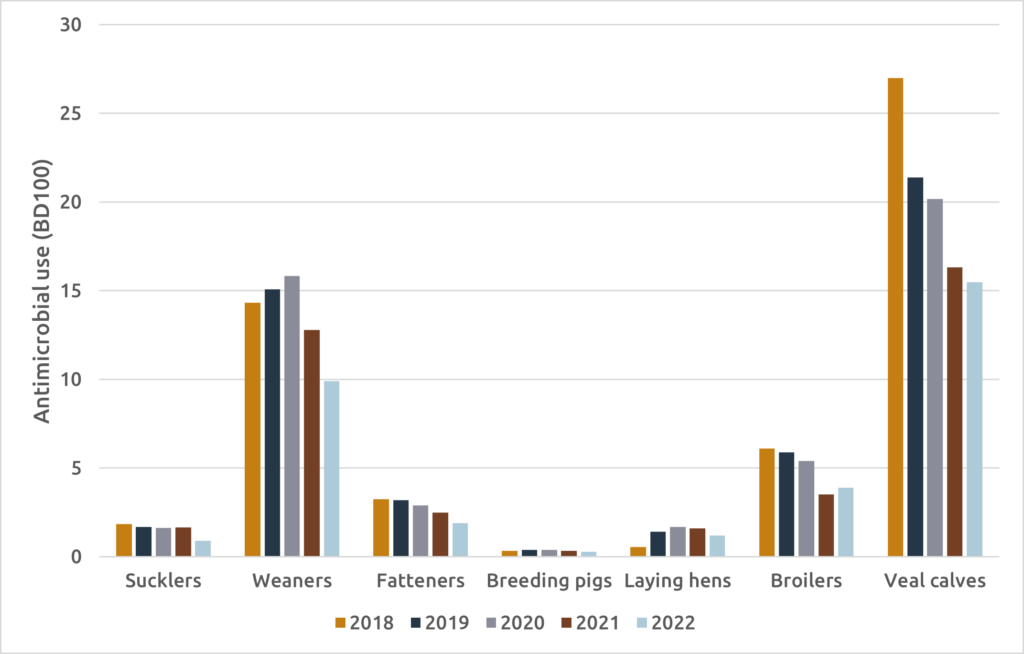
Figure 3: Antimicrobial use in BD100 in different animal species from 2018 to 2022 (source: BELMAP2023)
Antimicrobial resistance: divergent truths
Resistance trends vary among clinically significant human pathogens. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) has shown a decline in prevalence over the last decade, while E. coli exhibits an increase in resistant isolates to 3rd generation cephalosporins. Alarmingly, there’s a rise in multi-drug resistant (MDR) K. pneumoniae strains, potentially leading to higher mortality rates among vulnerable groups. Although resistance in older bacterial strains seems to be declining, newer, more dangerous strains are emerging.
In food-producing animals, commensal bacteria analysis reveals a different story. E. coli serves as the primary indicator, with fully sensitive strains found most often in beef cattle. The proportion of fully susceptible E. coli strains (pan-S) increased in fattening pigs and veal calves, while multi-drug-resistant (MDR) E. coli levels decreased in fattening pigs and broilers. Notably, industries with declining antibiotic usage also experienced significant decreases in resistance.
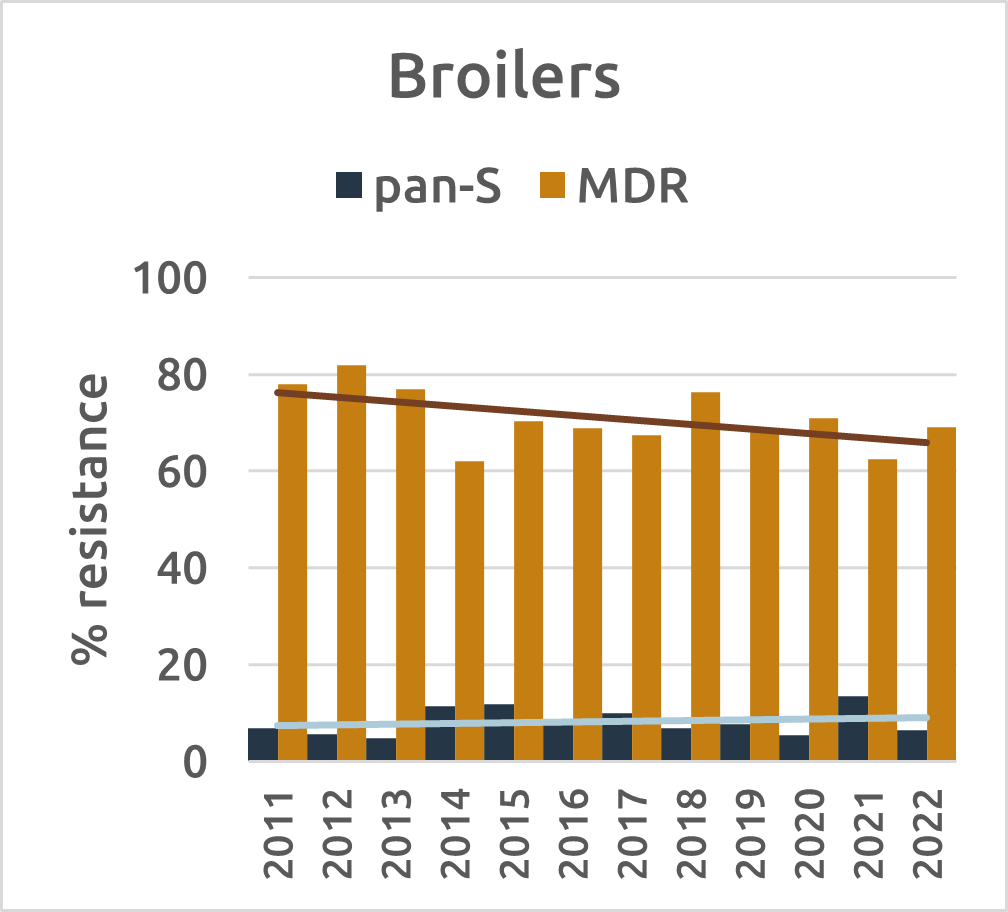
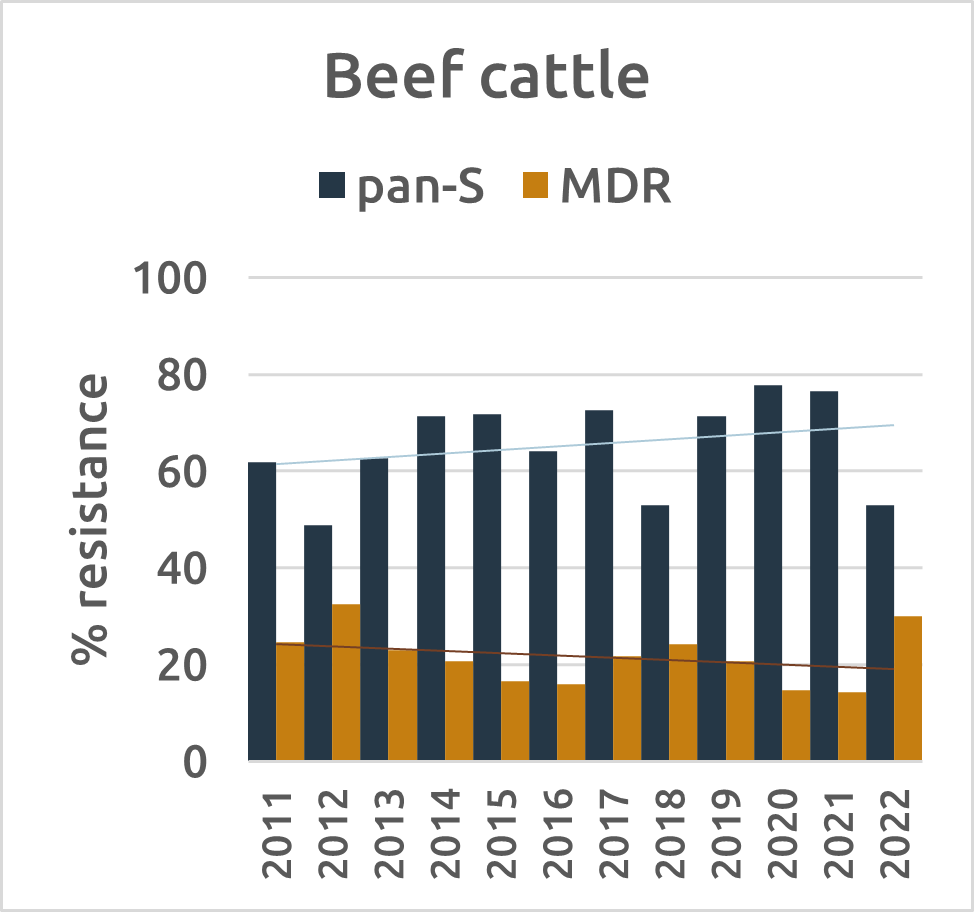
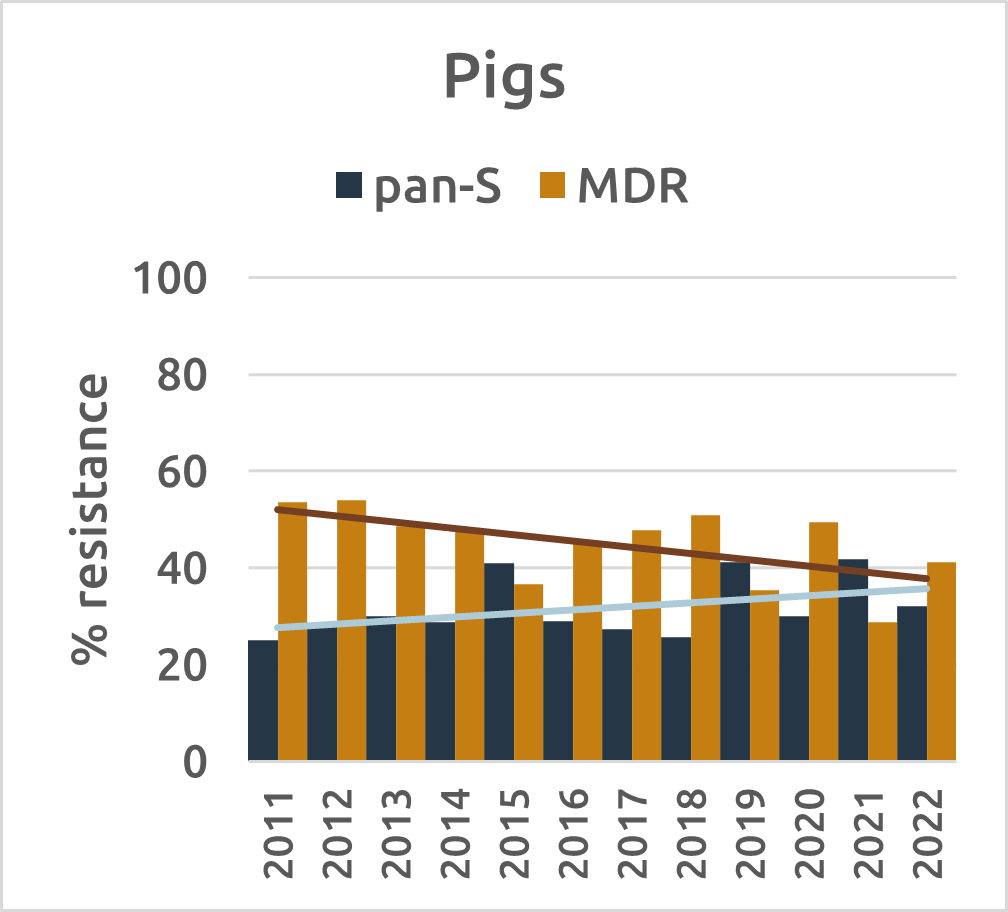
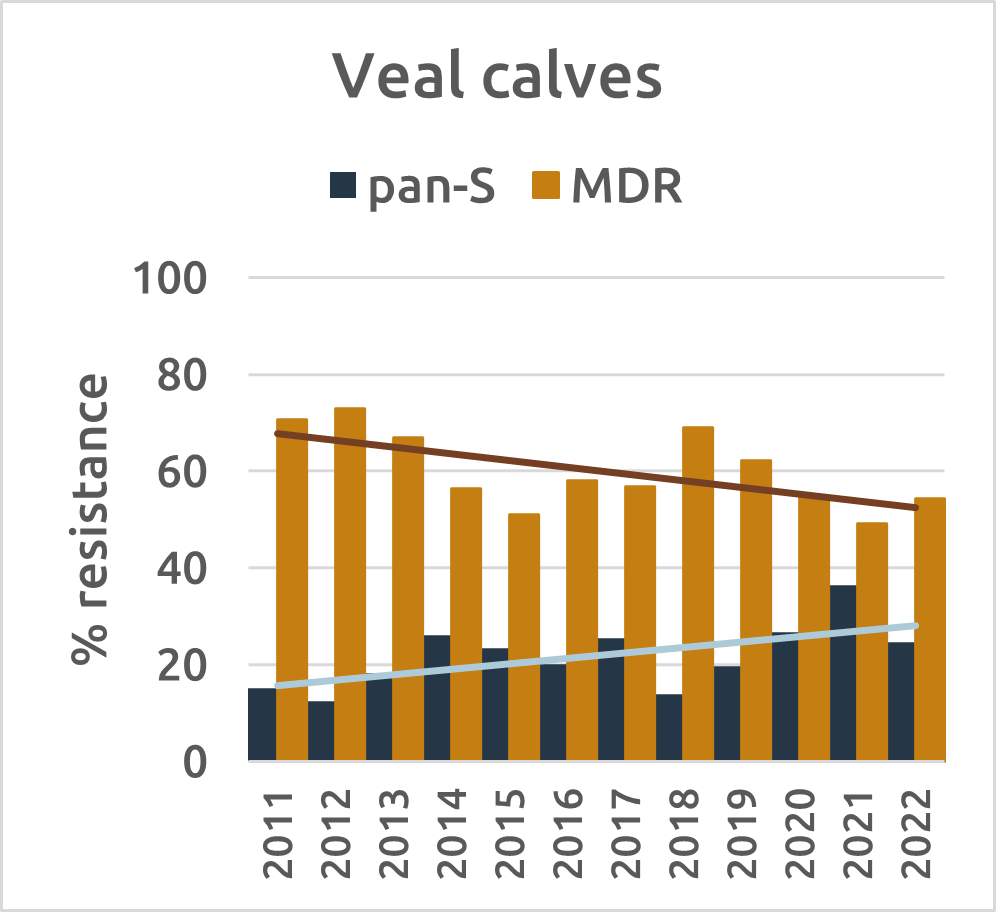
Figure 4: Evolution of resistance (%) for pan-S and MDR E. coli strains in broilers, beef cattle, pigs and veal calves (2011-2022) (source: BELMAP2023)
Livestock industry strategies
Reducing antibiotic use varies across species, but the focus remains on disease prevention. This involves three main aspects: vaccination, biosecurity, and overall animal health. Vaccination is highly effective in preventing outbreaks, while biosecurity measures limit exposure to bacterial pathogens, although implementation challenges differ among species.
Despite these challenges, significant efforts are being made. Next to these elements, environmental factors – such as climate, farm type and ventilation – also play a crucial role in the prevention of disease outbreaks. Additionally, ensuring good nutrition promotes animal health and reduces the need for antibiotics. Agrimprove is contributing to this by offering functional feed ingredients to limit antibiotic use. Overall, effective farm management and awareness of farm conditions are vital to reducing antibiotic consumption.
Conclusion
The veterinary industry is at the forefront of reducing antibiotic use and resistance. Its efforts have resulted in decreased antibiotic resistance, making Belgium an example for other nations to follow. Agrimprove is actively contributing ideas to combat antibiotic over-use and resistance, lending further support to this ongoing battle.